Decoding Precalculus: The Power of Symbols in Unlocking Mathematical Precision
Decoding Precalculus: The Power of Symbols in Unlocking Mathematical Precision
In the world of advanced mathematics, symbols are not mere shorthand — they are the precise language through which complex ideas are communicated, calculated, and mastered. Among the most essential tools in precalculus, these symbols form the backbone of logical reasoning, equation manipulation, and conceptual clarity. From exponents and fractions to roots and functions, precalculus symbols transform abstract concepts into actionable knowledge, enabling students and professionals alike to navigate intricate mathematical landscapes with confidence.
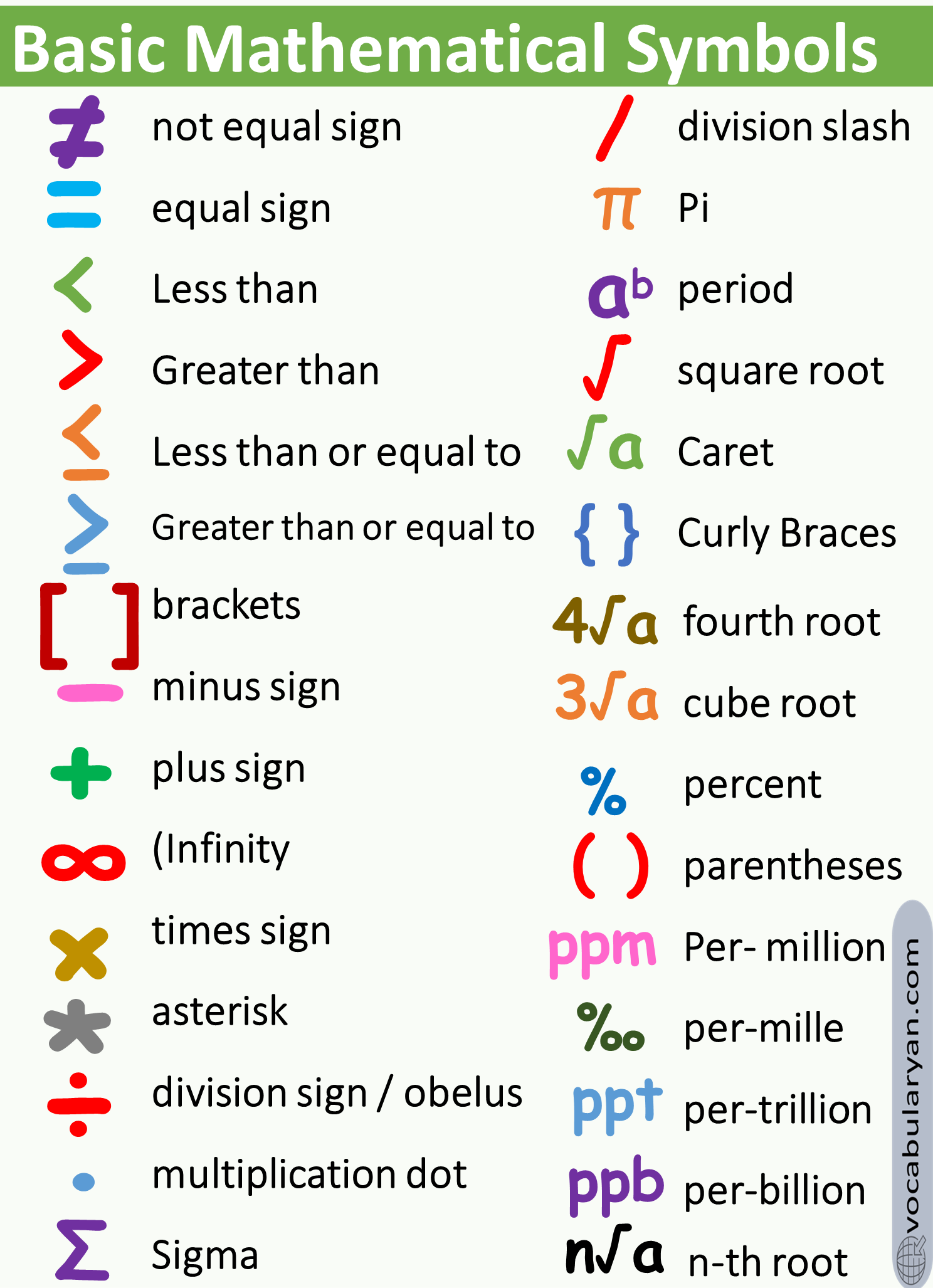
Understanding the Language: Core Symbols That Shape PrecalculusPrecalculus relies on a concise yet powerful set of mathematical symbols—each carrying specific meaning that governs how expressions are interpreted and resolved.
These symbols serve as the universal syntax that bridges intuition and precision. Central among them are the exponent notation (”), fractional powers and roots (x, √), absolute value | |, and the various function notation types including polynomial, logarithmic, and inverse functions.
For example, the expression x3 immediately conveys a cubic operation without ambiguity. Yet its depth extends further: when combined into limits, series, or calculus precursors, such symbols anchor foundational understanding.
Equally critical is the radical symbol √, which encapsulates symmetry and periodicity—particularly evident in expressions like √(−1), a gateway to imaginary numbers.
Basic fractions such as a/b and compound fractions ((a/b)c) coordinate operations across variables, while the placement of exponents—via superscripts—dictates order of operations in complex expressions. Within nested functions and continued fractions, every symbol preserves structural integrity, enabling scalable reasoning from algebraic foundations to advanced modeling.
Functions: The Pulse of Precalculus and Their Symbolic Markup
No exploration of precalculus symbols is complete without focusing on function notation—arguably the most vital linguistic layer. The ubiquitous f(x) notation not only declares input–output relationships but also encodes transformations, domain constraints, and asymptotic behavior.
Visualized on a graph, f(x) = 1/x reveals symmetry and discontinuities, demanding careful interpretation of horizontal asymptotes and intercepts.
Logarithmic and exponential functions—denoted as logb(x) and bx—are indispensable for modeling growth, decay, and scaling. Their inverse relationship exemplifies how symbolic precision uncovers deeper mathematical truths: iteration of bx undoes logb, a duality foundational to exponential equations and real-world phenomena like compound interest or radioactive half-lives.
Inverse trigonometric functions—arcsin(x), arccos(x), arctan(x)—demonstrate how specialized symbols extend continuity and range considerations. These not only standardize notation across textbooks and research but also prevent misinterpretation in calculus applications involving limits and derivatives.
Moreover, piecewise functions and absolute value notation |x| extend flexibility.
The absolute value symbol enforces non-negativity, critical in defining distance, error margins, and optimization problems. Together, these symbols create a symbolic ecosystem where complexity is reduced, clarity is enhanced, and logic drives discovery.
Algebraic Foundations: Exponents, Roots, and Fractions Under the Microscope
Exponential expressions—ranging from integer powers to irrational exponents—serve as the scaffolding for dynamic systems and asymptotic analysis. Consider (2x)5 vs.
25x5: misinterpretation risks cascade errors in expanded forms, underscoring the necessity of clear symbolic hierarchy.
Fractional exponents, such as x½, seamlessly unite roots and powers, enabling elegant rewriteings like x½ = √x. This notation not only simplifies notation but deepens conceptual fluency—students recognize square roots as ½-exponents, reinforcing connections between arithmetic and algebra.
Rational exponents further bridge discrete and continuous space: xm/n combines n-th roots and m-th powers, a notational wizardry essential in solving algebraic equations and modeling real-world growth patterns. Mastery here is not merely symbolic—it translates into computational agility.
Fractions in numerators and denominators carry their own weight: proper vs.
improper fractions, simplified vs. expanded forms, and rational expressions: (x + 1)/(x − 1) require symbolic precision to avoid domain errors and apply algebraic properties valid only when defined.
Logical and Transcendental Symbols: Bridging Discrete and Continuous Domains
Precalculus does not dwell solely in arithmetic—it ventures into logic and transcendence, where symbols like ∈ (element of), ⊂ (subset), and ℝ (real numbers) guarantee rigorous definitions. The inflation symbol → illustrates limits, a gateway to calculus💡, while e and π anchor exponential and circular functions in scientific modeling.
Roots and irrational numbers—especially √−1, which births i—expand the symbolic universe into complex plane, where geometry and algebra merge.
This expansion enables description of non-real systems, from oscillatory motion to electrical engineering circuits.
Transcendental functions—log10, sin(x), ex—rely on implicit but powerful notation that conveys periodicity, growth rates, and convergence behaviors. Their formal appearance in power series and differential equations reveals deep structural relationships beyond basic computation.
Significance extends to compound operations: parentheses preserve grouping, impacting order of evaluation; exponents atop parentheses override multiplication; bar notations denote inverses. Each symbol is a commitment to unambiguous logic.
Mastery Through Symbol Fluency: The Key to Precalculus Success
To truly grasp precalculus is to fluently interpret and wield its symbolic language.
These aren’t abstract marks—they are operational tools that dictate correct manipulation, prevent cascading errors, and unlock insight into advanced mathematics and science.
Consider solving x⁴ =



Related Post

<strong>Unlock Genomic Insights with Kbase: Transforming Bioinformatics Through Scalable Science</strong>

Unlocking Academic Success with Purdue Global Student Login

Dixon Technologies: The Owner and Their Impact – How A Visionary Owner Shapes a Global Force

