Define Pedigree: The Blueprint of Heredity That Shapes Life’s Inherited Legacy
Define Pedigree: The Blueprint of Heredity That Shapes Life’s Inherited Legacy
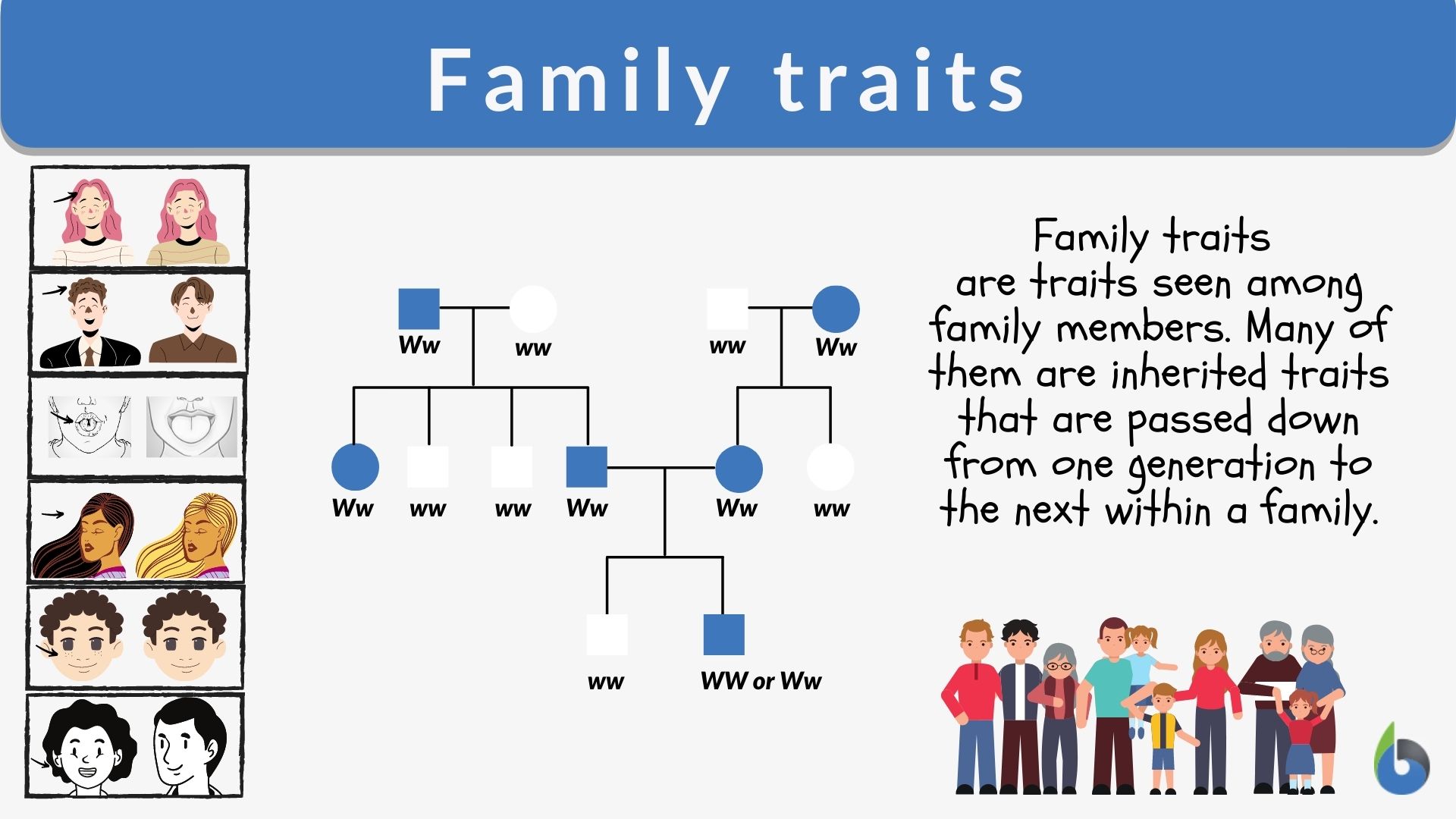
Pedigree stands as a foundational concept in genetics—a meticulous diagram mapping familial relationships and the transmission of inherited traits across generations. More than a mere chart, a pedigree serves as a visual chronicle of genetic continuity, vulnerability, and diversity within a family tree. Defined as a symbolic sketch illustrating bloodlines and the expression of heritable conditions, pedigrees are indispensable tools in medicine, research, and ethics, enabling precise tracking of dominant and recessive genes, sex-linked disorders, and chromosomal anomalies.
Their structured layout, integrating symbols, annotations, and time markers, reveals patterns invisible at first glance, turning complex inheritance into accessible, analyzable data. <
Horizontal lines connect partners, while vertical lines link parent to child, anchoring generational depth. Additional details are embedded through shading, lettering, or annotations—such as a shaded square to mark a genotype variant, or a superscript notation indicating a specific mutation.
Pedigrees are categorized by their scope and objective: - **Basic Pedigrees** document a single patient’s family history, focusing on key traits across two or three generations.- **Extended Pedigrees** span five or more generations, enabling analysis of long-term patterns, particularly valuable in studying rare genetic diseases. - **Sex-Linked Pedigrees** highlight X- or Y-chromosome trait transmission, crucial for conditions like hemophilia or color blindness. - **Risk Assessment Pedigrees** integrate statistical models to estimate recurrence probabilities, guiding clinical decisions and family planning.
The power of pedigrees lies not just in depiction, but in interpretation. For example, the consistent vertical transmission of a trait through males suggests an X-linked recessive pattern, whereas skipped generations with horizontal spread alert to autosomal dominant inheritance. Pedigrees reveal evolution over time.
Consider a generation where multiple individuals express a trait—this may indicate penetrance and variable expressivity, biological quirks often overlooked in simplistic models. <
Today, their use is governed by strict confidentiality and informed consent. Modern genetics has refined pedigree methodology with DNA sequencing, enabling molecular validation of family history predictions. Advanced algorithms now analyze vast pedigree datasets to identify novel gene-trait associations, accelerating discovery in rare disease research.
Structured pedigree charts empower clinicians to distinguish Mendelian patterns from multifactorial complexity. For instance, while cystic fibrosis follows a clear autosomal recessive course, conditions like heart disease or autism reflect intricate gene-environment interactions visible only through deep familial analysis. <
In education, pedigrees teach foundational genetics principles—how dominant alleles like Huntington’s disease letters through generations, or how consanguinity increases risks. Students and professionals alike rely on them to decode inheritance with precision. The precision of a pedigree’s interpretation is vital.
A single mislabeled individual or incorrect genotype symbol can distort conclusions, undermining diagnosis and care. Thus, constructing and analyzing pedigrees demands both technical accuracy and ethical vigilance. As genetic technologies evolve, pedigrees remain central—adapting to whole-genome data while preserving their role as visual anchors of inheritance.
They democratize complex biological concepts, making inherited risk tangible and actionable. From identifying carriers of sickle cell anemia to forecasting Alzheimer’s likelihood, pedigrees transform abstract genomic data into life-altering insights. Pedigree is not static—it is a living, evolving record at the crossroads of biology, medicine, and humanity.
Defined systematically, interpreted critically, and applied ethically, pedigrees illuminate the silent language of genes woven through generations, shaping how we understand, anticipate, and respond to heredity’s legacy.



Related Post
Samsung Free Vs. Android: Which Smartphone Operating System Truly Delivers?
<h1>Bactafuz Fusidic Acid Cream: The Powerful Treatment Redefining Skin and Soft Tissue Infection Management

Rockefeller Ingles: Pioneering Philanthropy and Smart Urban Innovation
Dan Futterman: The Visionary Voice Behind Cinematic Sound Design

