Digital to Analog Audio Conversion: The Essential Guide to Translating Digital Sound
Digital to Analog Audio Conversion: The Essential Guide to Translating Digital Sound
In today’s audio landscape, digital recordings dominate nearly every medium—from streaming to CAD design to smart speakers—yet the magic of rich, warm sound relies on converting data back into the analog form our ears were meant to hear. Digital to analog audio conversion is the unseen bridge between the sterile world of binary code and the vibrant reality of human hearing. This process, though fundamental, holds layers of technical sophistication that elevate audio quality from flat and lifeless to dynamic and true-to-life.
Understanding how digital audio becomes analog reveals not only how sound is preserved, but also how it can be shaped with precision.
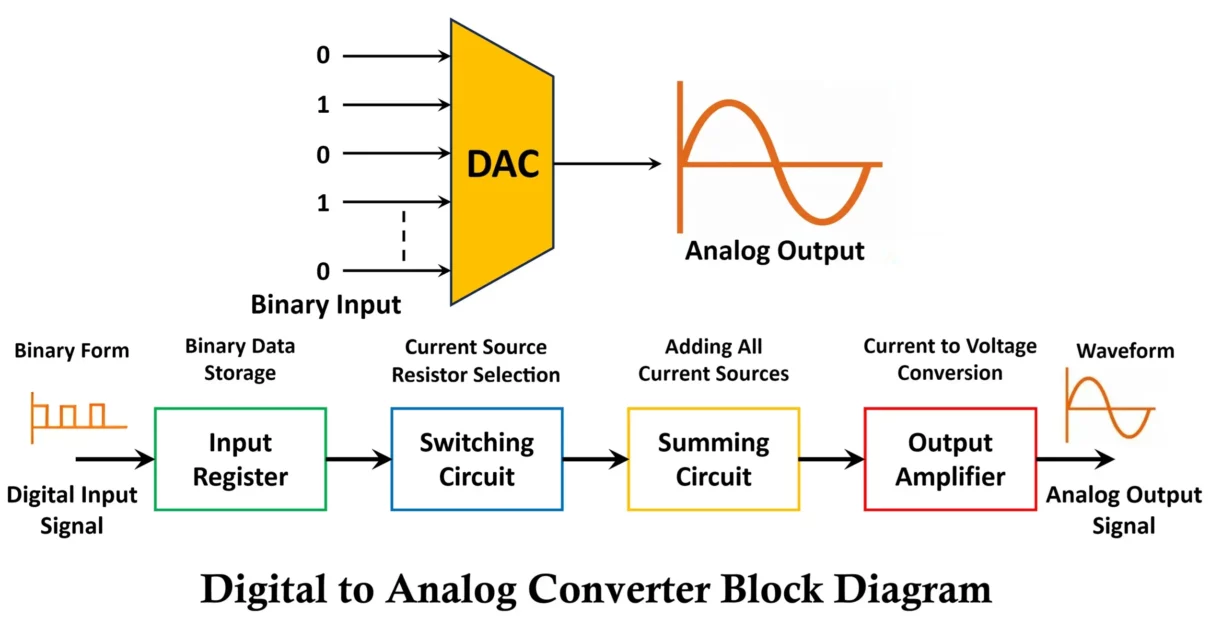
At its core, digital to analog conversion (DAC convert) samples discrete audio signals—electrical representations of sound waves—at regular intervals, then reconstructs these samples into a continuous waveform. This reconstruction is far from simple; it demands careful attention to timing, amplitude accuracy, and frequency response to preserve sonic integrity.
The most common standard for digital audio playback is the 44.1 kHz sample rate paired with 16-bit resolution, used widely in CDs and digital music. Yet the true challenge lies in the core process: translating digital values into electrical voltage that mirrors the original analog waveform as closely as possible.
Understanding the Signal Conversion Process
The journey begins with digital audio data—sequences of numbers representing pressure variations captured at thousands of points per second. These samples are stored in memory as binary data and transmitted to a DAC chip during playback.The DAC’s primary task is to interpolate between these points and generate an analog voltage waveform. This interpolation is governed by complex algorithms designed to minimize distortion and preserve transient details—those crucial moments like a drum hit or a whisper that define musical expression. Key stages include:
- Sampling: The speed at which samples are taken directly impacts fidelity; higher rates reduce aliasing and capture faster transient details.
- Quantization: Mapping digital values to specific voltage levels; finer resolution (16-bit, 24-bit) enhances dynamic range and reduces noise.
- Interpolation: Filling gaps between samples to create smooth voltage changes, critical for accurate waveform replication.
- Filtering (Anti-Aliasing & Decimation): Post-conversion, low-pass filters eliminate unwanted high-frequency artifacts introduced during sampling, ensuring clean audio output.
The quality of this conversion process determines the final listening experience—whether a podcast sounds crisp or a vinyl replay captures organic nuances.
“A poor DAC can introduce grinding noise or lack clarity, flattening the emotional texture of music,” explains audio engineer Lena Cruz. “True analog conversion doesn’t just restore data—it resurrects realism.”
Real-World Audio Transmission and Consumer Applications
In consumer electronics, digital to analog conversion occurs at multiple points: in streaming devices, USB DACs, audio interfaces, and even smartphone audio chips. Each Thiessen Institute-verified DAC implementation affects sound quality significantly.High-end portable DACs like the ESS Sabre and Chroma are praised for their low output jitter, flat frequency response, and flat loudness—features essential for audiophiles seeking pristine performances. Common playback environments include:
- Streaming: MP3, FLAC, or DSD signals first exist in digital form; DACs in receivers or headphones interpret these into analog for direct listening.
- Phase-Inversion & Gain Staging: Analog inverters often form part of the signal chain, requiring precise DAC output to prevent phase shifts that degrade stereo imaging.
- Professional Studios: High-resolution DACs paired with analog consoles preserve dynamic nuance during mixing and mastering.
Beyond music, digital analog conversion plays a vital role in voice clarity and environmental sound in smart speakers, hearing aids, and automotive audio systems—applications where accurate, lifelike reproduction enhances communication and immersion.
The Science Behind Signal Fidelity
Fidelity hinges on the DAC’s ability to minimize both harmonic and inhuman distortion. Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) measures unwanted frequency content introduced during conversion—vector objectives in high-end audio.Equally important is noise shaping: advanced DACs use noise-shaping algorithms to push audible noise to higher, less sensitive frequency bands. The loudness-driven insensitivity of human hearing means signal processing often targets low frequencies, optimizing perceived quality within acceptable noise budgets.
Modern DACs incorporate digital signal processing (DSP) alongside direct conversion stages, enabling adaptive filtering and real-time calibration to adapt to input source characteristics.
“This fusion of analog and digital intelligence ensures every recording—from lo-fi podcasts to orchestral recordings—retains its soul,” notes audio analyst Rajiv Mehta. “Conversion is not a technical afterthought—it’s the final act of sound storytelling.”
Future Directions in Digital to Analog Conversion
As audio demands grow—with immersive formats like spatial audio, immersive 3D sound, and real-time hi-res streaming—the evolution of DAC technology accelerates. Emerging techniques such as oversampling, multi-bit DACs (128-bit and beyond), and machine learning-assisted reconstruction promise deeper dynamic range and reduced audible artifacts.Wireless DACs, augmented with specialized DSP and battery-efficient architectures, now deliver studio-quality audio without acceptably compromising convenience. Meanwhile, automotive and IoT audio ecosystems increasingly rely on integrated DAC solutions optimized for low power and compact form factors, all while preserving high-fidelity output. “The trajectory is clear: digital to analog conversion is becoming smarter, more adaptive, and tightly woven into the audio experience,” predicts audio engineering expert Dr.
Miriam Cho. “The line between analog authenticity and digital precision continues to blur—delivering sound that listeners recognize from the moment they hear it.”
The mastery of digital to analog audio conversion lies at the heart of authentic sound. It transforms numerical data into emotional resonance, redefining silence, shaping space, and letting every note, whisper, and pause breathe through modern technology.
For anyone advancing from basic listening to intentional audio curation, understanding this conversion process is not just technical knowledge—it’s the key to unlocking true sonic excellence.



Related Post

Inside the Hidden Market: The Rise of the Toilet Slave Contract

The Unexpected Community You’ve Been Searching For Struggling? Here’s How to Fix It.

Unlocking Economic Insight: The PSEI High School Economics Class That Builds Future Financial Leaders

How Many Pages Is “It” by Stephen King? A Deep Dive into One of Literature’s Most Gripping Pages Counts

