How One Tragedy Changed Aviation Safety: The Jal Airlines Flight 123 Disaster
How One Tragedy Changed Aviation Safety: The Jal Airlines Flight 123 Disaster
On August 12, 1985, a Japan Airways Boeing 727 suffered a catastrophic failure mid-transit, marking one of the deadliest air accidents in aviation history. Jal Airlines Flight 123—and its devastating crash—exposed critical flaws in aircraft design, maintenance protocols, and pilot training, reshaping global aviation safety standards for decades. The disaster not only claimed 520 lives but ignited a worldwide reevaluation of flight safety systems.
The flight departed Matsumoto Airport bound for Tokyo at 11:57 JST, carrying 524 passengers and 7 crew across 14 stopped destinations.
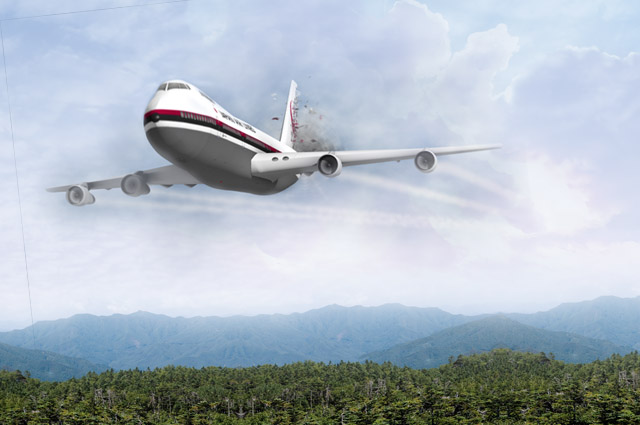
Within 12 minutes of takeoff, a section of the rear pressure bulkhead collapsed, triggered by a defective stainless steel rivet joint in the Aircraft Structural Integrity System. This seemingly isolated failure unleashed a rapid decomposition of the rear pressure cabin—an unintended explosive decompression—that severed control cables and damaged flight systems. Pilots lost control as the aircraft entered a steep descent, unable to respond to the catastrophic structural failure.
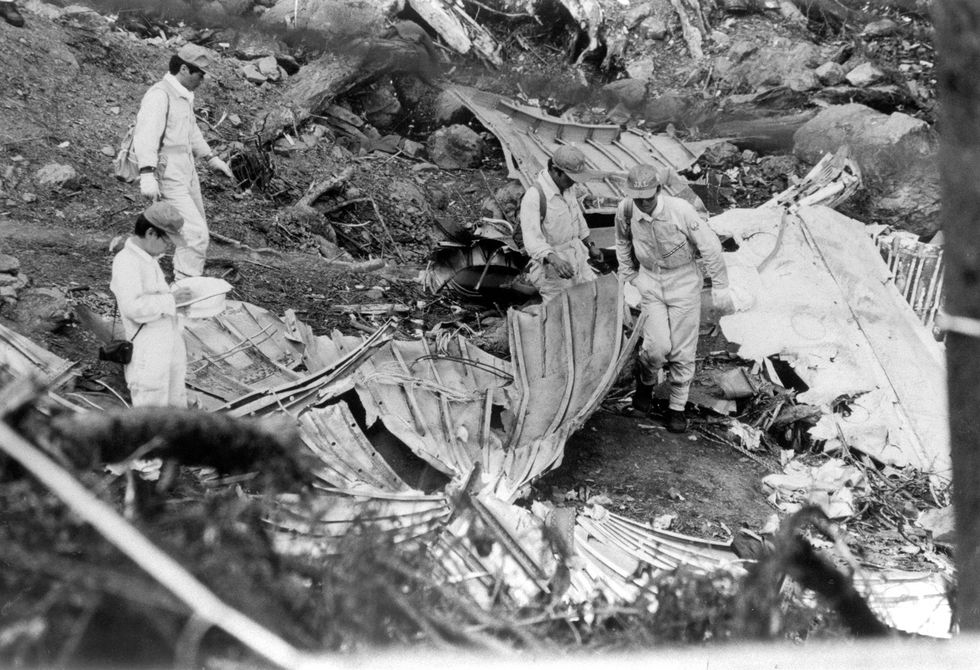
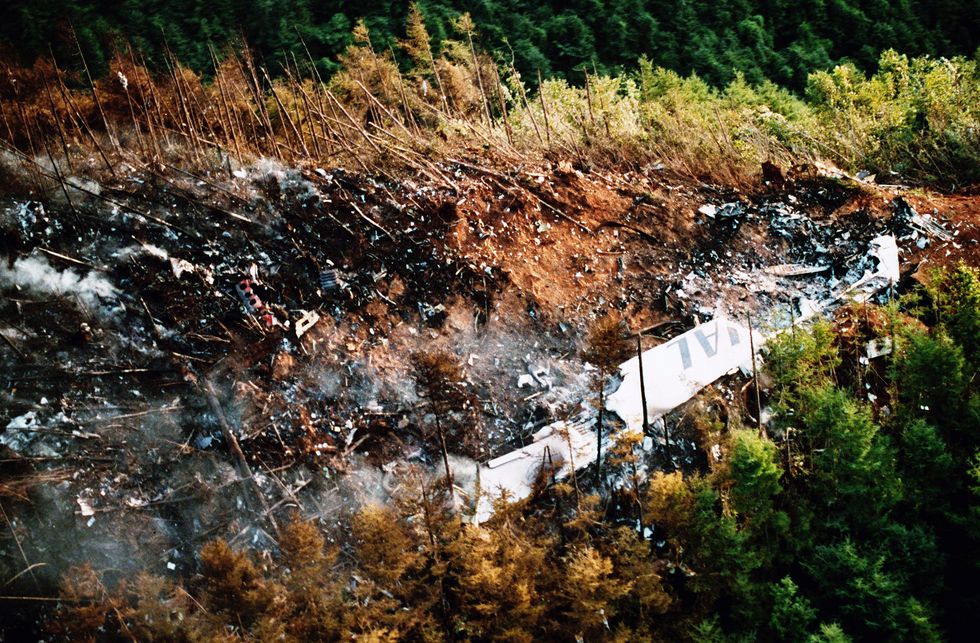
Despite emergency attempts to level the plane, the aircraft crashed into Ogawa Village in Gunma Prefecture, killing all aboard.
The Hidden Failures Behind the Collapse
The crash revealed systemic oversights in aircraft engineering and oversight:
- Defective Structural Component: Investigations confirmed that a 1960s-era rivet joint design—using a “high-strength” but inferior captive rivet—weakened under cyclic stress, ultimately failing without visible warning. This flaw had been documented internally but not adequately addressed.
- Lack of Structural Integrity Oversight: Japan’s aviation authority had not enforced rigorous periodic inspections for pressure cabin stress points. The bulkhead’s deterioration went undetected for approximately six months after initial foam contamination was observed.
- Inadequate Piloting Response Protocols: Crew training did not emphasize immediate acknowledgment of sudden decompression effects on flight control, and checklists failed to account for rapid cabin pressurization failure.
Technical analyses by Japanese and international investigators pinpointed the rupture zone at the 48th to 85th forward pressure bulkhead, where repeated pressurization cycles fatigued the rivets.
Once ruptured, the resulting rapid pressure loss rendered aerodynamic control nearly impossible—leaving pilots with mere seconds to react.
Aftermath: Infinite Changes to Aviation Regulation
The disaster’s wake was seismic:
The incident prompted the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and national regulators to mandate stricter aviation safety frameworks. Boeing and other manufacturers revised structural certifications, demanding redundant stress-testing of critical joints. Japan updated its airworthiness directives, requiring quarterly inspections of rear cabin pressure bulkheads and advanced nondestructive testing for rivet joint integrity.
Jal Airlines itself faced intense scrutiny.
Though the carrier had operated safely for decades, the accident tested public trust and led to profound operational reforms. Pilots’ training curricula were overhauled to simulate sudden structural failures, integrating emergency decompression response drills and enhanced crew communication under duress. Emergency response coordination also improved, with crisis management now prioritizing rapid evacuation and trauma-informed passenger care.
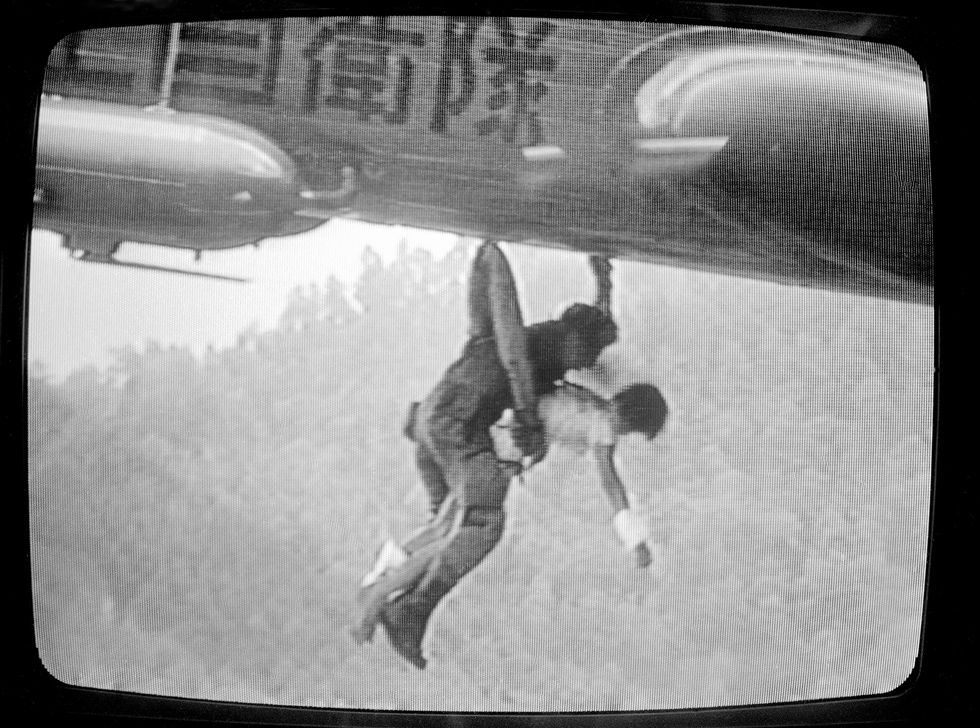
The physical aftermath lingered: a debris field spanning over 2 square kilometers slowed rescue operations for days.
For families, identification became a prolonged ordeal—mass mortality ruled out personal recognition, forcing forensic teams to rely on dental records and DNA analysis. The event underscored not just technical vulnerabilities, but the human cost embedded in every structural flaw.
Long-Term Legacy on Global Flight Safety
Jal Airlines Flight 123 remains a stark reminder of aviation’s fragility when design, oversight, and human readiness falter. Its legacy endures in modern cockpits: automated monitoring of pressure systems, refined rivet specifications, and tighter regulatory oversight now prevent similar failures.
Airlines worldwide now conduct stress lifecycle assessments for airframes, treating structural integrity as an ongoing engineering commitment, not a one-time certification.
The crash also elevated public awareness of flight safety. Passengers now expect transparent maintenance records and robust safety audits, while regulators enforce accountability across borders.
The tragedy catalyzed a culture of proactive failure prevention—pilots report unreported anomalies, inspectors challenge complacency, and manufacturers innovate with enhanced diagnostics.
Why the Memory of Flight 123 Still Matters
More than a single accident, Flight 123 is a cornerstone in aviation safety’s evolution. It exposed the silent, structural weaknesses hidden within airframes—and revealed how human and systemic factors converge in catastrophe.
The 12-minute descent after bulkhead failure became a paradigm for rapid threat response and system redundancy. Every subsequent safety upgrade, every trained pilot’s response, and every regulatory mandate traces its roots to that July afternoon in 1985. In understanding this disaster, the aviation world not only honors its victims but strengthens the foundation of safe flight for generations to come.




Related Post

Unraveling The Life Of Mary Beth Haglin: A Journey Beyond the Screen

Is Kinsey Schofield Married? The Quiet Truth Behind the City Lights Spin—And Speculations About Prince Harry That Have Taken the Internet by Storm
Who Owns BBC News Indonesia? Unpacking the Layers of Ownership and Influence
At 68, Shawn Killinger Stands at the Frontlines of Ageing Advocacy—A Voice for a Shifting World

