Inside the Cell: How Animal Cell Vacuoles Power Vital Functions
Inside the Cell: How Animal Cell Vacuoles Power Vital Functions
Pivotal to maintaining cellular balance yet often overlooked, vacuoles in animal cells serve as dynamic organelles far more than passive storage units. Far from being simple containers, these membrane-bound sacs actively regulate internal environment, manage waste, and facilitate intracellular transport. Far from static, dynamic vacuoles enable animal cells to adapt, survive, and function with remarkable precision—making them indispensable to cellular life.
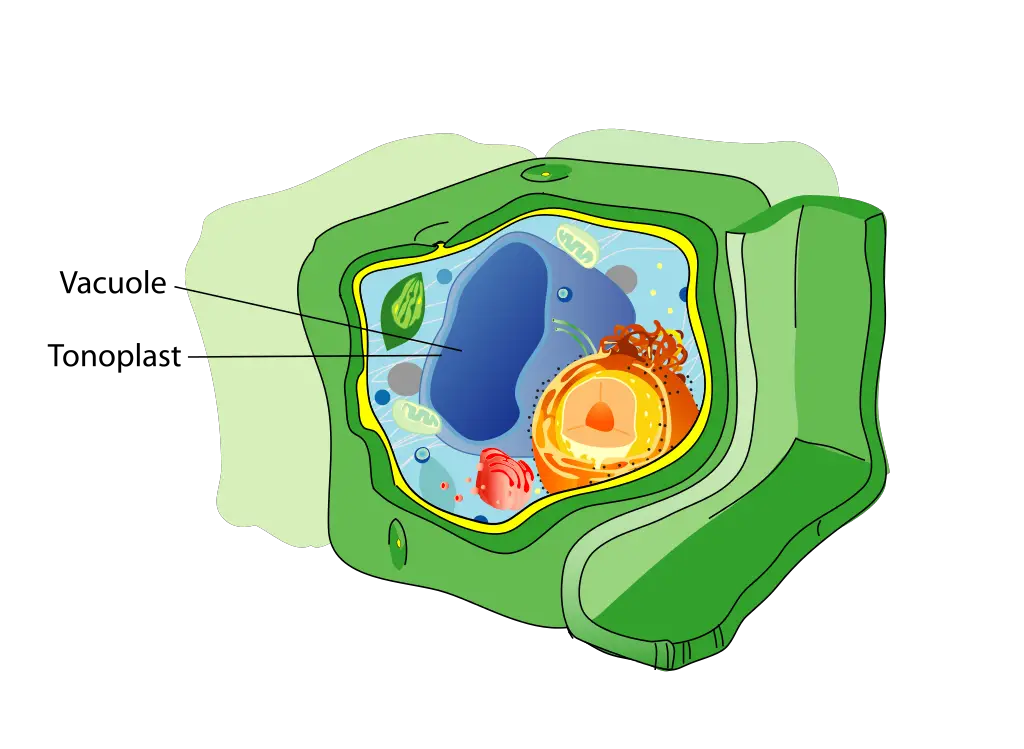
Defined as large intracellular vesicles enclosed by a lipid bilayer membrane, vacuoles accumulate water, ions, metabolites, and digestive enzymes, enabling the cell to achieve homeostasis. Unlike the rigid cell wall of plant cells, animal vacuoles are flexible and capable of dynamic reshaping, allowing them to expand, fuse, and shuttle cargo with rapid efficiency.
The Adaptive Nature of Vacuoles in Animal Cells
One of the most striking features of vacuoles is their adaptability.In professional biologists’ terms, vacuoles function as both **compartmentalized workstations** and **logistical hubs**. They maintain osmotic equilibrium by actively transferring water and solutes in and out of the cytoplasm, preventing cellular bursting or shrinking. When environmental conditions shift—such as changes in extracellular ion concentration—vacuoles swiftly adjust volume through regulated osmotic flow, a process essential for cell survival.
They collect and sequester metabolic byproducts and foreign particles, directing them for degradation or expulsion. This role enhances metabolic efficiency by isolating toxic materials and concentrating them in a single compartment, reducing cellular damage and improving overall function.
Waste Processing: Vacuoles as Intracellular Recycling Centers
Intracellular digestion within vacuoles mirrors functions seen in lysosomes but with distinct advantages.Unlike lysosomes, which are primarily lysosomal enzymes optimized for breaking down macromolecules, vacuoles incorporate a broader enzymatic arsenal, capable of degrading diverse biological materials. Their flexible membrane enables direct fusion with endosomes and peroxisomes, allowing timely oxidation, hydrolysis, and recycling of proteins, lipids, and other cellular debris. This integrated detoxification and recycling system is especially critical in high-metabolic-rate tissues such as liver and kidney cells, where rapid processing of toxins and worn-out organelles sustains cellular integrity.
_Vacuoles act as multidimensional command centers, merging storage, digestion, and transport functions with unmatched versatility, unlike simpler organelles with narrower roles. Beyond waste management, vacuoles drive critical transport mechanisms. Through endocytosis and exocytosis, they facilitate directed movement of substances across the cell membrane. By encapsulating large molecules or particulates, vacuoles bypass the limitations of membrane diffusion, ensuring precise, efficient delivery of nutrients, hormones, and signaling molecules to their intended cytoplasmic destinations.
Their dynamic movement—steered by motor proteins along microtubules—positions vacuoles strategically near mitochondria or the nucleus, optimizing energy supply and regulatory control.
The Building Blocks of Vacuole Function
The functional sophistication of vacuoles stems from their structural and biochemical design. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer embedded with transport and fusion proteins, vacuoles maintain a neutral internal pH conducive to enzymatic activity.Ion channels and proton pumps regulate internal chemistry, preventing degradation of sensitive cargo until targeted release. Enzymatic contents vary by cell type, reflecting functional specialization:
- Nutrient storage: Glycogen, lipids, and ions stored in hepatic and muscular vacuoles supply energy during metabolic demand.
- Digestive vacuoles: Found in phagocytic cells like macrophages, these sequester and dismantle engulfed pathogens.
- Signaling compartments: Specific vacuoles concentrate signaling molecules, enabling rapid intracellular communication.
Their fusion with endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus enables rapid cargo exchange and quality control, ensuring only properly folded proteins reach their destinations. In neurons, vacuole trafficking supports axonal transport, critical for nerve impulse conduction.
From Microscale Regulation to Organismal Impact
The operational efficiency of vacuoles ripples through multicellular systems.In epithelial cells lining the gut, vacuolar activity optimizes nutrient absorption by concentrating digested molecules before transport into the bloodstream. In muscle cells, vacuolar modulation of calcium and ion balance supports precise contractile responses. In neurons, timely clearance of cellular debris via vacuole-mediated autophagy prevents toxic buildup, preserving synaptic function and preventing neurodegeneration.
Collectively, these roles illustrate a sophisticated network of intracellular processes driven by far more than passive containment—vacuoles are active, responsive, and regulatory powerhouses embedded within every animal cell.
The Dynamic Future: Vacuoles in Health and Disease
Understanding vacuole function reveals new frontiers in medicine and biotechnology. Dysfunction in vacuolar acidification or cargo sorting is linked to lysosomal storage disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and impaired immune responses.Emerging therapies aim to restore vacuole activity, offering hope for conditions once deemed irreversible. Vacuoles continue to captivate scientists as master regulators of cellular life—flexible, intelligent, and indispensable. As research deepens, their hidden complexity reaffirms: within every animal cell lies a microscopic powerhouse driving survival, adaptation, and order in life’s smallest networks.
Far from inert compartments, vacuoles embody the elegance of cellular engineering—where structure, transport, and metabolism converge to sustain life at the most fundamental level.



Related Post

From Boredom to Breakthrough: How Thestripesblog.com Explodes with Irresistibly Engaging Content—and Why Zoewebs Stands Out

Unblocked Tomb Of The Mask: The Virtual Arena Where Masked Battles Rage Unhindered

Grace Boor, Johnsonwright, and the Next Generation: Trailblazers Redefining Modern Entertainment Through Tech and Youth

Unlocking Meaning Stock: How Businesses Are Valuing Purpose Beyond Profit

