Master Chemistry Battery Design with the Pogil Batteries Answer Key: A Student’s Essential Guide
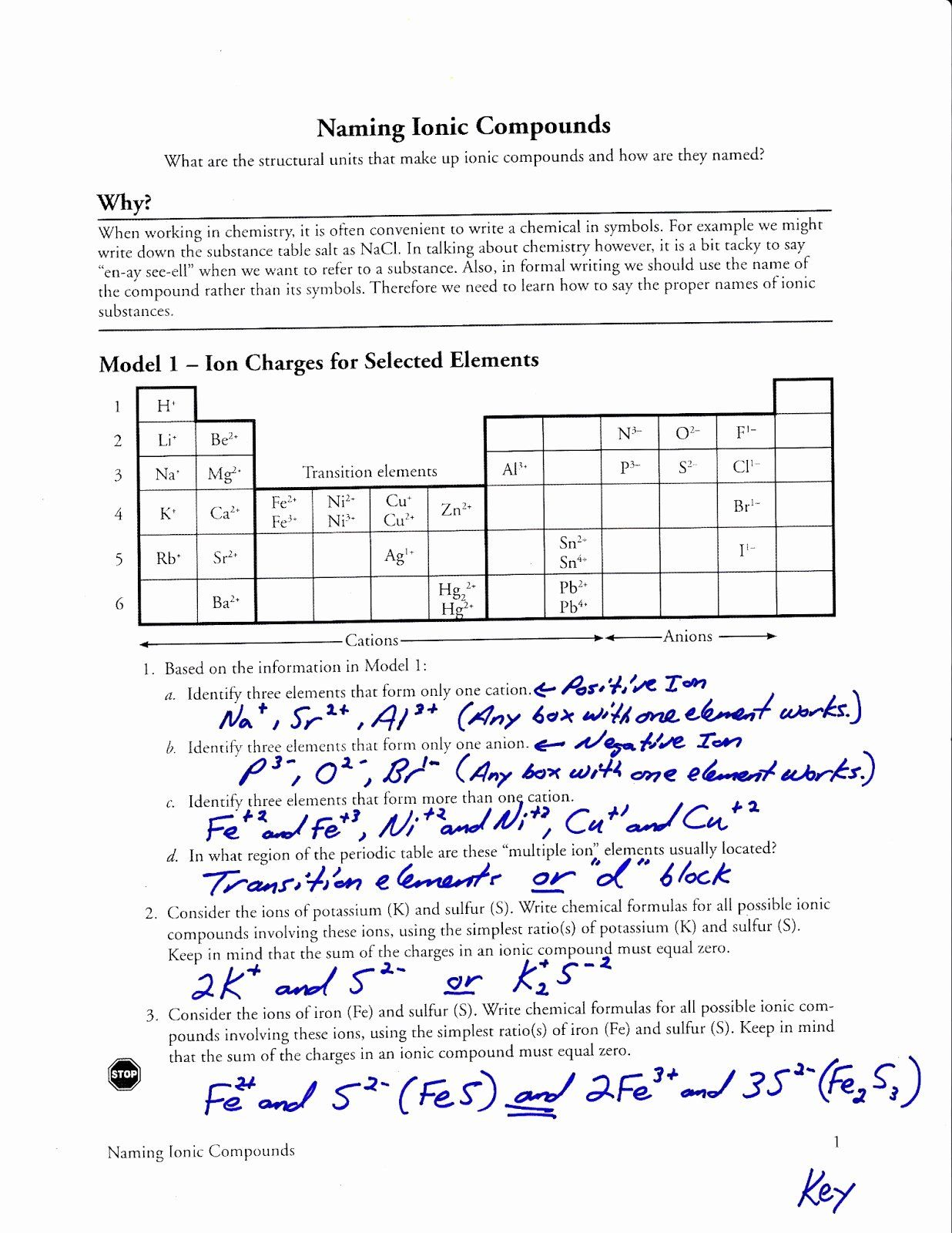
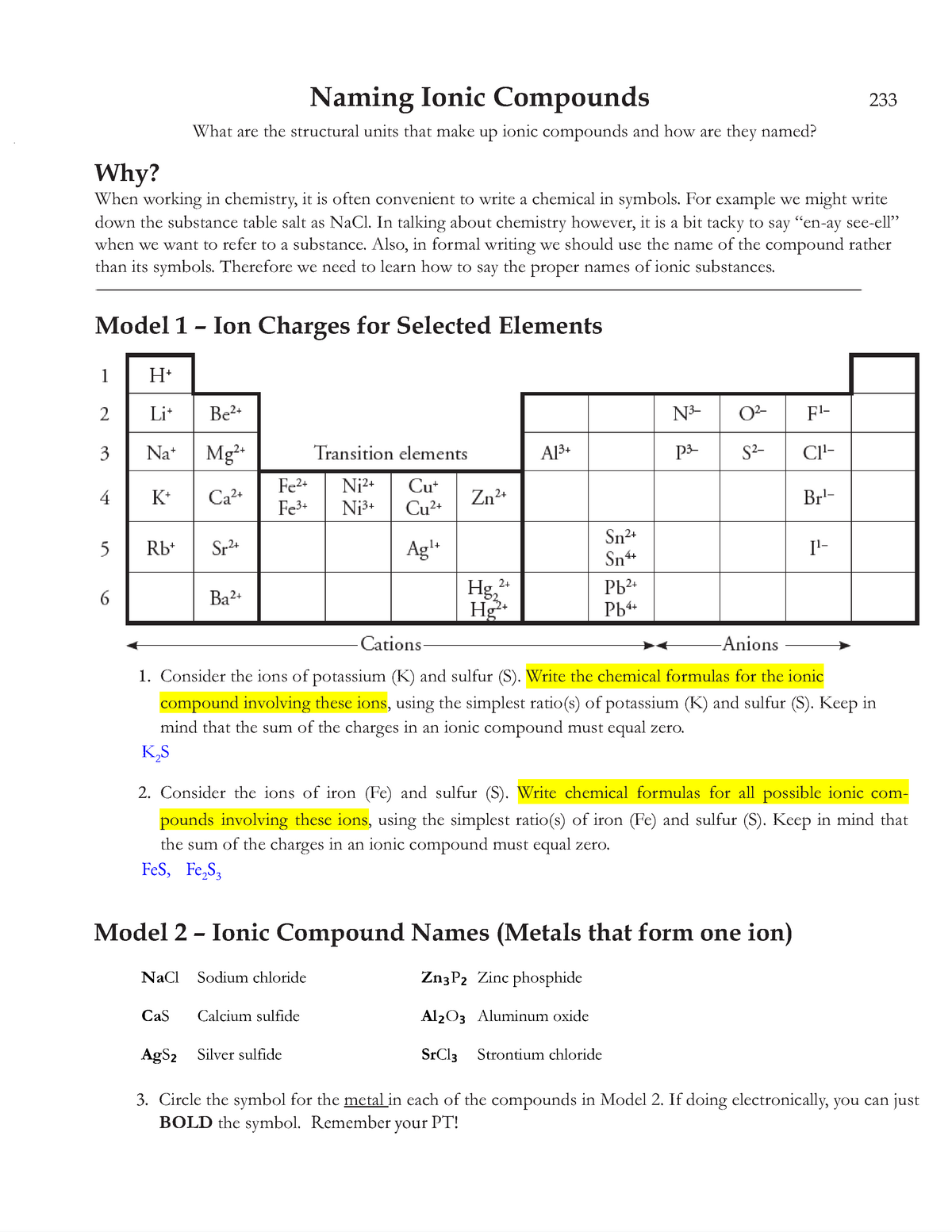
Master Chemistry Battery Design with the Pogil Batteries Answer Key: A Student’s Essential Guide
Understanding electrochemical cells and batteries is fundamental to modern chemistry, yet grasping electron flow, redox reactions, and cell potential can challenge learners. The Pogil Chemistry Batteries Answer Key transforms this complexity into accessible, digestible insights—equipping students with tools to analyze bond formation, energy conversion, and real-world battery performance. This practical resource bridges theory and application, helping students master key concepts through structured inquiry and precise problem-solving.
Central to the Pogil Batteries Answer Key is its focus on core electrochemical principles embedded in each battery system.
Students dissect the chemistry behind common cells—such as the zinc-carbon and lithium-ion batteries—learning how oxidation and reduction reactions drive electron transfer. The answer key emphasizes identifying anode and cathode materials, tracking electron flow, and calculating standard cell potentials using standard reduction potentials from referenced tables. It reinforces critical thinking by connecting atomic structure and ionic behavior to macroscopic energy output.
Core Circuit Concepts: Electron Flow and Redox Reactions
The battery is not merely a device; it is a dynamic chemical reactor where redox chemistry powers electron movement.
The Pogil materials clarify this process by guiding students through step-by-redirected electronic flow:
This meticulously mapped electron transfer forms the basis of voltage generation. The answer key reinforces these ideas through guided questions asking students to sketch electron dot diagrams and interpret redox half-reactions. For example, in a zinc-copper cell, Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ (oxidation) and Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu (reduction) illustrate how chemical energy becomes usable electrical energy.
Understanding redox potentials is equally vital.
The Pogil batteries answer key equips learners to compare standard reduction potentials—such as Cu²⁺/Cu (+0.34 V) and Zn²⁺/Zn (−0.76 V)—enabling prediction of spontaneous electron flow. By calculating E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode, students quantify cell voltage, linking atomic properties directly to functional performance.
Battery Components and Their Roles
The Pogil Batteries Answer Key emphasizes the interdependence of cell components: electrodes, electrolytes, and separators each shape battery efficiency and stability.
- Electrodes: The anode (electron source) often uses metallic zinc in alkaline cells; the cathode, typically copper or manganese dioxide, accepts electrons.
The differential reactivity between anode and cathode drives sustained electron flow.
- Electrolyte: Typically acidic (Zn-carbon) or alkaline (nickel-cadmium), electrolytes facilitate ion migration—Zn²⁺ or H⁺ ions shuttle between electrodes to maintain charge balance.
- Separator: A porous barrier prevents physical contact between electrodes while permitting ionic conductivity, avoiding short circuits.
This detailed breakdown enables students to evaluate trade-offs: high-capacity electrodes (e.g., lithium) boost voltage but risk instability, while separators enhance safety but may reduce conductivity. The answer key challenges learners to assess how design choices influence real-world battery life and safety.
From Theory to Practice: Applying the Answer Key in Real-World Scenarios
Translating theoretical knowledge into practical problem-solving defines proficiency with the Pogil batteries approach. Students confront authentic challenges:
• Predicting Electrode Participation: Given a cell system involving magnesium, silver sulfate, and iron ions, learners identify which species behave as anode and cathode using standard potentials—Mg → Mg²⁺ + 2e⁻ (oxidation) dominates over Fe³⁺ + e⁻ → Fe²⁺ (reduction).
• Calculating Cell Voltage: Applying E°cell = [E°(Cu²⁺/Cu) – E°(Zn²⁺/Zn)] = (0.34 – (–0.76)) = 1.10 V, students verify theoretical outputs against experimental data.
• Analyzing Efficiency and Practical Limits: Discussions explore how internal resistance, polarization, and side reactions reduce real cell performance compared to ideal models—linking chemistry to engineering design constraints.
These exercises embed same-day application, ensuring students don’t just memorize formulas but develop analytical judgment essential for advanced studies and innovation.
Critical Components of the Pogil Answer Key
The Pogil Chemistry Batteries Answer Key stands out for its scaffolded, inquiry-driven format.
It provides: - **Stepwise problem breakdowns:** Sequential guidance from electron transfer analysis to voltage calculation prevents cognitive overload. - Contextual feedback: Explanations clarify not just “what” but “why,” such as why high-stability electrolytes reduce corrosion. - **Comparative data: Table comparisons


Related Post

Inside the Hidden Market: The Rise of the Toilet Slave Contract

The Unseen Threads: Unraveling the Relationship Between Peyton List and Jacob Bertrand

Paulo Londra’s Tour: A Global Revelation That Sells Over 500,000 Tickets in Just Days

Unlocking Mlifeinsider: The Ultimate Guide to Navigating the Data-Driven Loyalty Ecosystem

