Master Your Life One Tiny Habit at a Time: Lessons from the Atomic Habits Free Ebook
Master Your Life One Tiny Habit at a Time: Lessons from the Atomic Habits Free Ebook
Behavior change is often misunderstood as a matter of willpower or motivation, yet widespread failures in self-improvement reveal a deeper truth: lasting transformation stems from the compound power of small, consistent actions. The free auto-enrolled ebook *Atomic Habits*, distilled from James Clear’s proven framework, offers a mastery of how incremental changes create extraordinary results. At its core, the book distills a revolutionary idea: progress is not driven by radical overhauls, but by precise, repeatable habits embedded into daily life.
This article unpacks the science and strategies from the ebook, revealing how atomic habits—those small, unnoticed decisions—collectively reshape identities, boost productivity, and unlock long-term success.
James Clear’s principle, “You do not rise to the level of your goals; you fall to the level of your systems,” serves as the foundation of the *Atomic Habits* approach. The ebook argues that sustainable change originates not from grand ambitions but from designing simple, reliable routines that compound over time.
“Breakdown the breakthroughs into habits made of tiny behaviors,” Clear states—emphasizing that transformation begins with managing the system, not just the outcome. This concept challenges common misconceptions about discipline and motivation, shifting focus to environment design and automaticity.
Identify the Identity Behind the Habit
A pivotal insight from the ebook is that effective habits are anchored in identity, not just intent.Instead of setting goals like “I want to exercise more,” the framework urges users to reframe behaviors to reflect who they wish to become—“a runner” or “a disciplined learner.” This identity-first mindset transforms habits from isolated actions into expressions of self. As Clear explains, “Routines are the compound interest of self-improvement. Small improvements repeat daily, yielding explosive results over months and years.” By aligning actions with a clear personal identity, individuals create intrinsic motivation that endures setbacks.
To apply this, ask: “What kind of person do I want to become because of this habit?” Write this identity statement explicitly and tie daily behaviors to it. For example, “Because I’m a healthy person, I eat balanced meals and move consistently,” embeds the habit within a meaningful role, strengthening commitment far more than external rewards or pressure.
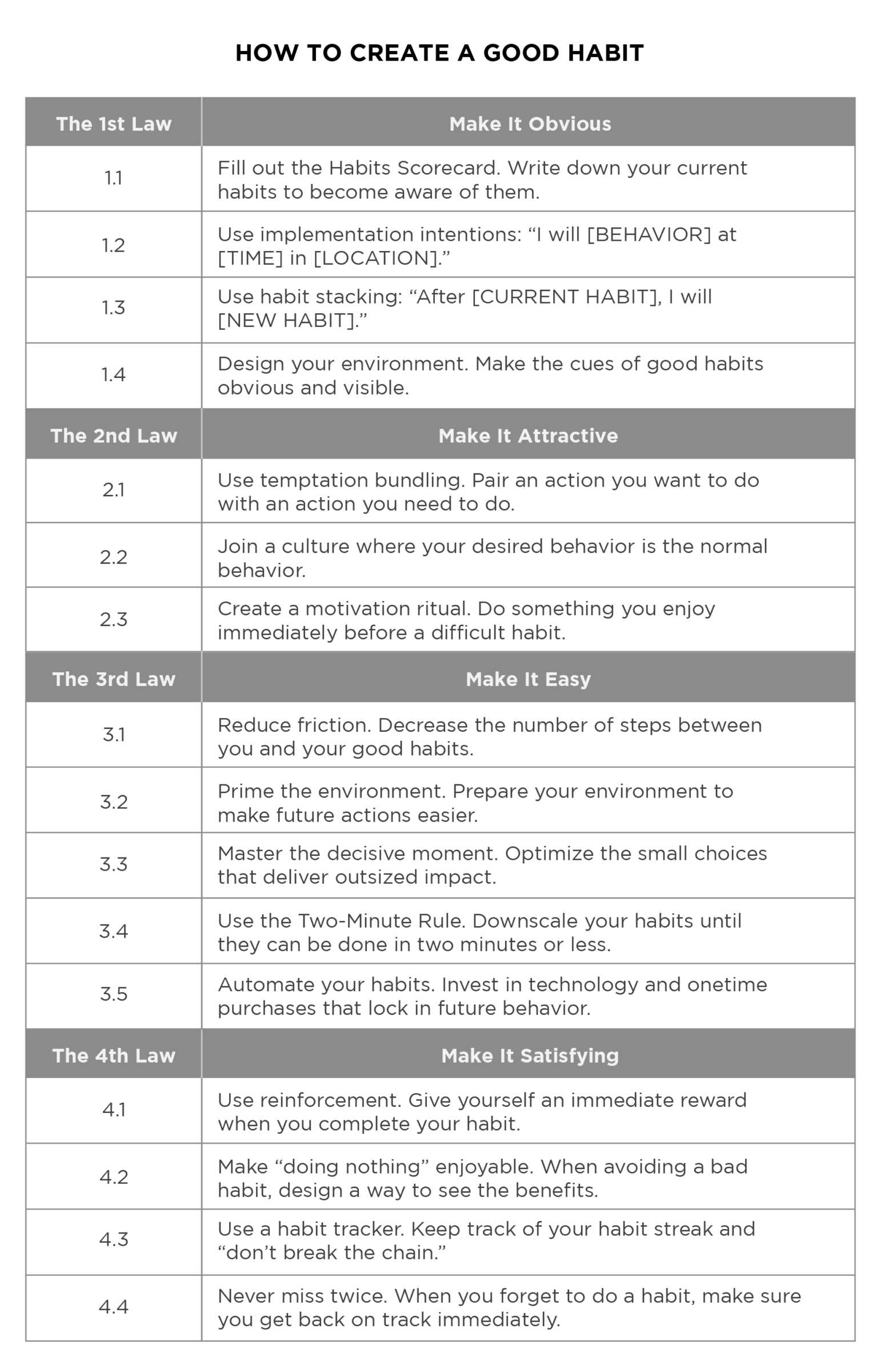
Design Habits to Be Obvious, Attractive, Easy, and Satisfying
The *Atomic Habits* ebook introduces a four-step framework—CUE, CRAVING, RESPONSE, REWARD—to engineer habit formation.Clear breaks down each element with precision: - **Make it Obvious**: Design cues that trigger action—place running shoes by the door, set phone reminders, or keep study materials visible. - **Anchor to Existing Habits**: Link new behaviors to established routines (habit stacking), such as flossing after brushing teeth. - **Make It Attractive**: Connect habit completion to a desired outcome—visualize the feeling of accomplishment or associate the habit with pleasure.
- **Make It Easy**: Reduce friction. If a habit feels hard, scale it down—just five push-ups count; you can always increase later. - **Ensure Immediate Gratification**: Pay off the habit quickly with small rewards—check a box on a habit tracker, enjoy a moment of relaxation, or note progress immediately.
When habits satisfy these four criteria, they become self-perpetuating. The brain learns to crave the ease and reward, reducing resistance and increasing follow-through. This system turns intention into automaticity without relying on motivation alone.
Leverage the Two-Minute Rule to Overcome Procrastination
One of the most accessible tools in the ebook is the Two-Minute Rule: start any new habit by committing to just two minutes of action. The idea is to lower the barrier so small that starting becomes effortless. For example, “read one page of a book,” “do two push-ups,” or “write a single sentence in a journal.” Because two minutes feels trivial, people rarely refuse—yet consistent execution builds momentum.After just days, the habit habitually extends itself as the brain associates the activity with completion, not effort.
This rule counteracts the common barrier of overwhelm. Instead of “I need to write a whole article,” the actionable step is “write one sentence.” Over time, these micro-commitments accumulate.
Studies cited in the ebook show that tiny, frequent actions rewire neural pathways, making larger goals feel attainable. “You do not implement monumental change. You implement micro-moments,” Clear observes—moments that, multiplied over weeks, become monumental progress.
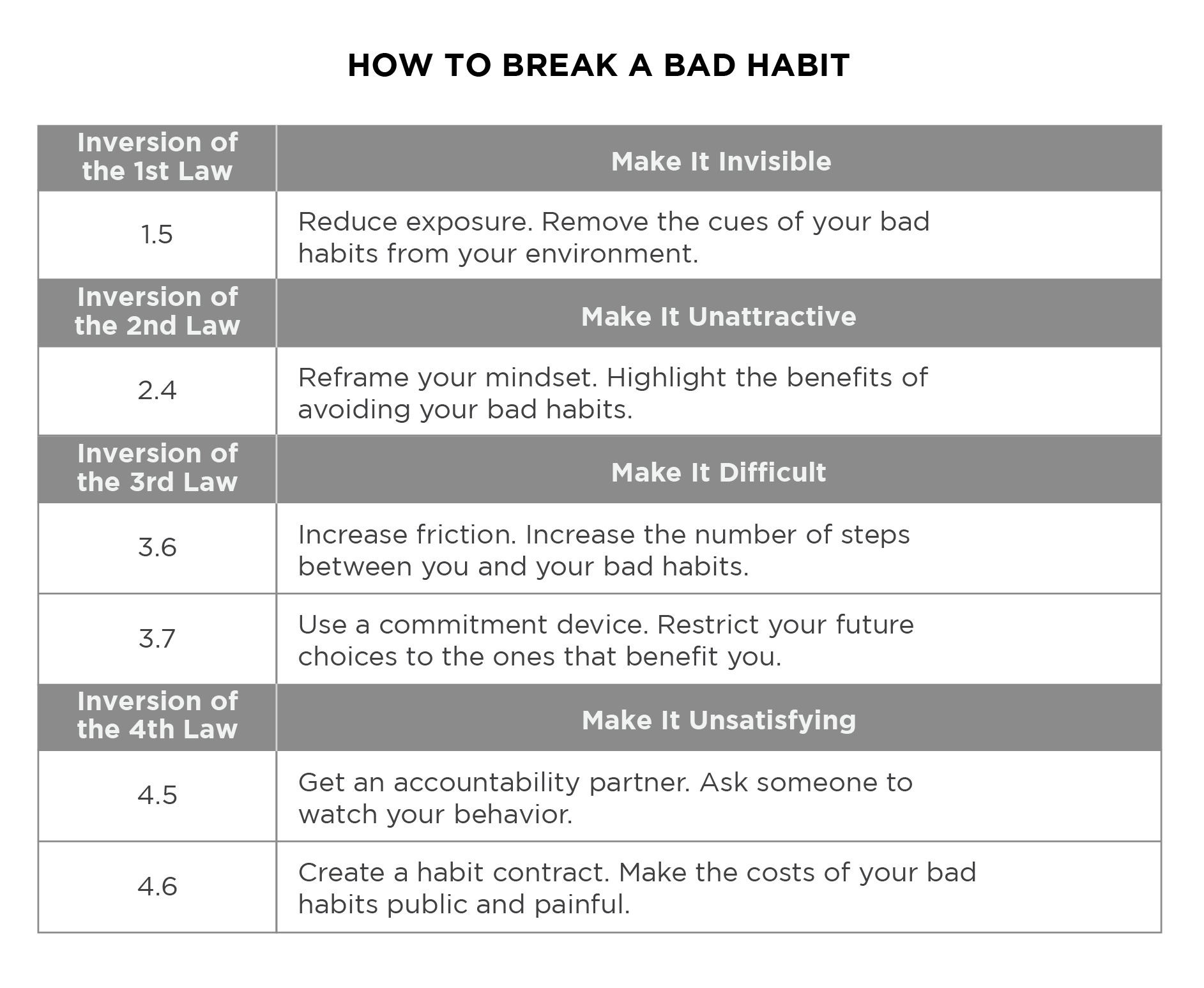
Optimize Your Environment to Eliminate Bad Habits
Ambition alone cannot sustain change. The *Atomic Habits* ebook emphasizes that success depends largely on managing your environment to support desired behaviors and defang obstacles. Environments either enable or sabotage habits—behavioral psychologist BJ Fogg’s principle applies powerfully here: people do what is easy, not necessarily what they intend.Clear urges readers to audit their surroundings: remove temptations and amplify cues for success. For instance, keep junk food out of sight to reduce snacking; organize workspaces to prioritize focus over distraction.
Similarly, social environments shape behavior.
Engage with communities—online or offline—that reinforce positive habits. If anyone in your orbit values learning, you’re more likely to read daily. Conversely, distance yourself from influences that encourage inaction.
Environmental design thus serves as a silent architect of behavior, reducing choice fatigue and making the right habit the easiest one to follow.
Track Progress with Visual Systems
Monitoring habits transforms abstract goals into tangible progress. The ebook strongly advocates for visual tracking—habit stackers use calendars, apps, or simple checklists to mark daily completion.Seeing a growing streak of checkmarks provides immediate psychological reinforcement and creates a powerful visual reminder of consistency. This practice boosts self-efficacy and fuels motivation, particularly during moments of doubt.
Real data strengthens accountability.
Graphs, journals, or apps that record habit frequency encourage reflection on patterns and triggers. Over time, users detect monthly fluctuations, identify slippage points, and adjust strategies proactively. For example, if morning meditation drops on weekends, the user might schedule it earlier or prep materials the night before.
Visual feedback turns isolated actions into measurable progress, embedding discipline into identity.
Use Identifiable Rewards—not Just Future Incentives
A common mistake in goal-setting is relying on distant, intangible rewards—gradual health improvements or long-term career success. Clear warns this underm

Related Post

Is Intel i3 Good for Gaming? Unveiling Performance, Real-World Usage, and Future-Proofing

Sumire Karaage Roll: The Culinary Art Behind a Food Wars Feast

Project 64 Reveals the Switch Pro Controller: The Precision Edge That Redefines Nintendo Switch Gameplay

Bunnie Xo Naked: Redefining The Aesthetic of Raw Vulnerability in Streetwear

