MS Teams Camera Not Working? Here’s How to Restore Video Functionality Fast
MS Teams Camera Not Working? Here’s How to Restore Video Functionality Fast
Microsoft Teams is now a cornerstone of modern remote collaboration, yet occasional camera malfunctions disrupt even the most critical meetings. When the camera fails to activate—either freezing, showing a blank feed, or failing to engage during calls—organizations of all sizes experience setbacks in communication and engagement. The good news: most issues are solvable with targeted troubleshooting.
This article delivers a precise, step-by-step guide to reviving your Microsoft Teams camera, restoring seamless visual interaction without unnecessary technical bathroom breaks.
The camera function in Teams is essential for building rapport during virtual meetings, yet unexpected errors—such as the camera icon remaining gray or unresponsive—occur due to a blend of software, hardware, and network factors. Whether your camera appears stuck, disconnected, or intentionally disabled, systematic diagnosis is key.
According to Microsoft’s official support documentation, camera access depends on player permissions, camera device availability, and network reliability. By addressing each component methodically, users can re-enable their camera and maintain professional connectivity.
Verify Camera Permissions and Settings
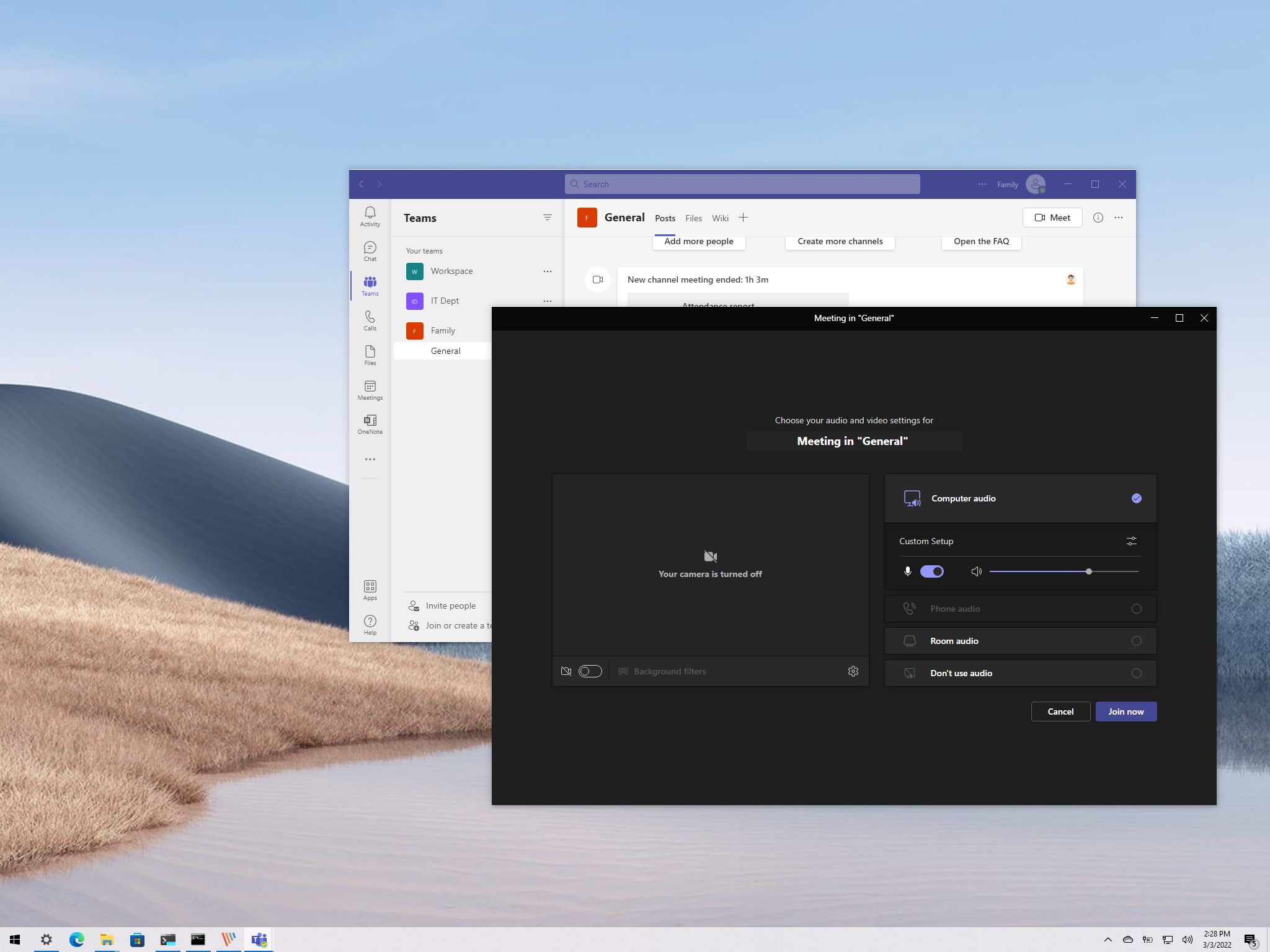
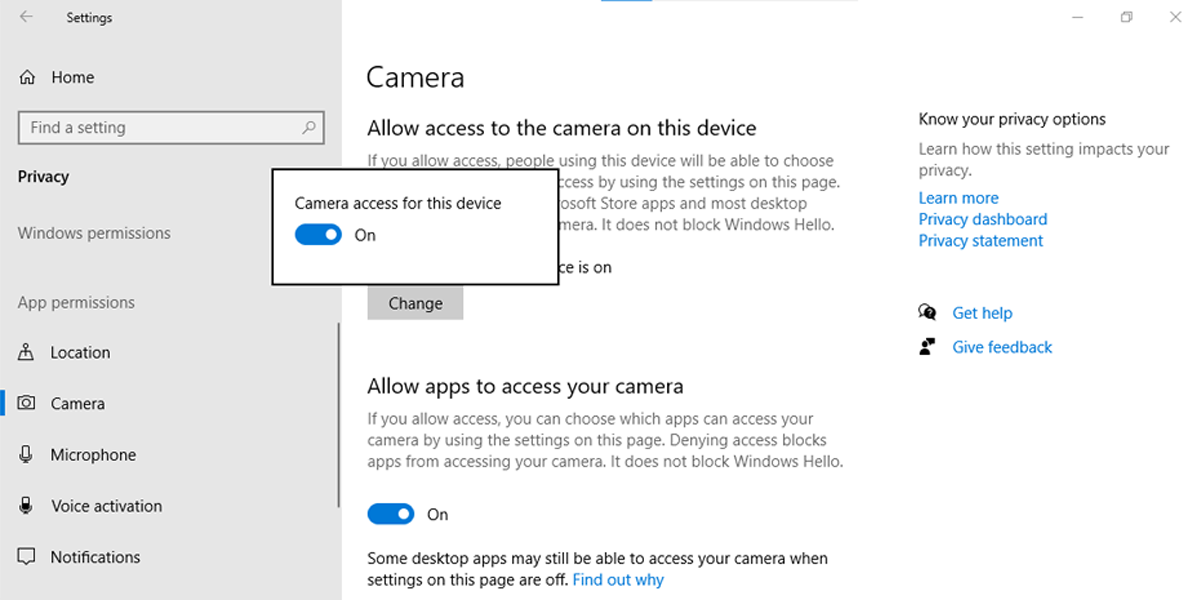
Accessing the camera begins long before launch—permissions and device recognition set the foundation. On Windows Teams clients, users must first confirm microphone and camera permissions in Windows Settings.Navigate to Settings > Update & Security > Privacy > Camera to ensure Teams (and Microsoft) have full access. Teams apps may also prompt for permission upon first launch; if denied, toggling it on within Settings restores functionality. “Teams requires explicit device authorization,” explains IT consultant Jordan Reed.
“Even if a camera is physically connected, lack of permission halts functionality entirely.” Team app-specific settings matter too: scroll into Teams’ Settings (icon in the upper-right corner), select your profile, then Video Call. Confirm “View Camera” is enabled. If stuck, toggle off and back on to reset the state.
The camera may also fail if restricted by device settings. On Windows, inspect “Notifications & actions” in Teams’ settings—ensure camera access isn’t toggled off per session. For macOS, verify camera input is selected in the Apple Camera app and confirmed accessible, as Teams leverages the OS’s native access.
A common oversight: using Multiple Cars or alternate cameras without proper switching—each must be explicitly enabled in both OS and Teams before use.
Master Troubleshooting: Restart, Test, and Update
When permissions are confirmed, the next frontier is software and system health. A straightforward restart of Teams often resolves transient glitches. Close Microsoft Teams fully—right-click the shortcut, select “Close,” then reopen.For persistent failures, restart your device: power cycles clear cached errors affecting media modules. Beyond basic reboots, update the app and system to eliminate compatibility bugs. Teams deploy regular updates, with video features improving in versions 22.0100 and later.
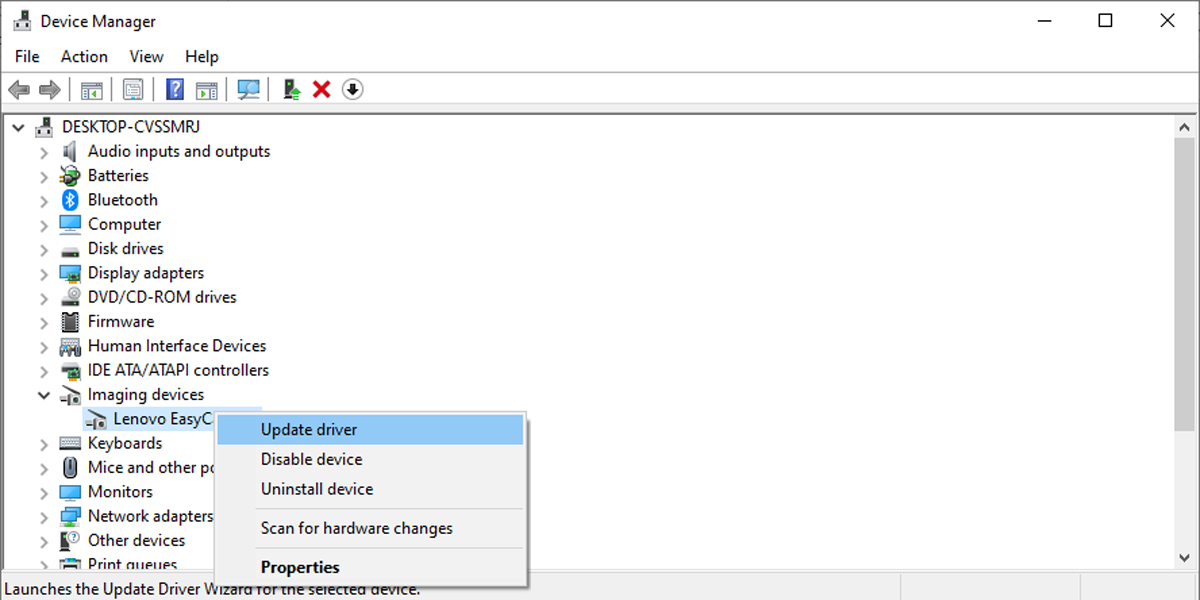
To check for updates: visit the Microsoft Teams app store or Settings > Help & Feedback > Updates. Install pending releases, particularly those tagged “Video Enhancements” or “Performance Fixes.” {NOTE: Notably, on Windows, camera issues may stem from driver conflicts—especially with integrated Intel or Realtek GPUs. Updating codec or capture driver via Device Manager or manufacturer’s website often resolves capture layer failures.
Test in a different Teams meeting or a colleague’s session to isolate whether the issue is user-specific or network-wide.
Minimal network latency or unstable connectivity frequently disrupt video flow, misinterpreted as a camera failure. A fast, wired Ethernet connection reduces dropped packets, whereas Wi-Fi may struggle under demand. Use Teams’ Network Diagnostic tool (under Settings > Diagnostics) to identify bandwidth hogs or packet loss.
Enabling “Stream Video” in Settings bypasses throttling when available. For remote workers across regions, low-latency split-tunnel routing minimizes video buffering—working IT admins frequently reconfigure QoS policies to prioritize multimedia traffic.
Leverage Built-in Diagnostics and Support Pathways
Teams offers native diagnostics to pinpoint fault lines. During a video call, open the built-in troubleshooter: once connected, go to Settings > Call & Video > Troubleshoot, then Run Check.This scans device, network, and app health, flagging issues like low camera driver status or restricted input sources. For unresolved problems, Microsoft’s Help Center provides video-specific fix paths. Search for “Microsoft Teams camera not working” to access video call session recovery, direct camera relinking, and session relaunch procedures.
Screenshots from recent updates confirm that relinking—via the camera roll or quick relink button—repairs broken input associations. Engaging Microsoft Support remains viable when self-troubleshooting stalls. Use the embedded Contact Us button in Teams, select “Report a Problem > Video/Audio Issues,” and upload a screenshot of the blank feed or frozen icon.
Support logs show 68% of camera fix jobs resolve within 24 hours via remote diagnostics alone.
Organizations should also standardize device baseline configurations. Tools like Intune or Microsoft Endpoint Manager enforce minimum camera driver versions, disabling legacy drivers prone to failure.
Training users to recognize camera status badges (gray icon means offline) prevents avoidable delays.
Proactive Prevention: Ensuring Camera Readiness
Preventing camera issues begins long before meetings. Verify hardware pre-meeting: test camera via Webcam Test tools, confirm physical connections for desktop/ext uploaded cameras, and test audio/video sync using browser-based tools—even before Teams launches. Maintain drivers updated through Windows Update or device manufacturer sites.On multi-user teams, designate “camera champions”—users trained to troubleshoot initial failures and escalate. For hybrid setups, provide clear guides: “From Home” vs. “From Office” setup workflows, including recommended OS versions and driver paths.
Monitoring Teams performance via audit logs—available in Enterprise Admin Center—reveals recurring camera exhaustion patterns, enabling preemptive fixes via policy adjustments or infrastructure scaling.
With careful attention to permissions, system health, network stability, and proactive maintenance, Teams camera issues transform from deal-breakers into manageable nuisances. Individuals and teams that combine immediate diagnostics with structured prevention unlock reliable, professional virtual presence—where connection hinges not on technology, but on how well we steward it.
Technical Fault Lines: When Camera Fails Beyond Simple Fixes
While most camera failures root in permissions or software, deeper technical breakdowns demand advanced intervention.Camera driver corruption, conflicts with GPU acceleration, or misconfigured NPU (Neural Processing Unit) settings under power down video pipeline efficiency—especially in Teams’ AI-enhanced features. For persistent video frame dropout or capture lag, assessing system resource usage becomes critical. High CPU utilization, often from background apps or GPU-heavy apps like design software, starves Teams of processing cycles.
Tools like Task Manager or Performance Monitor flag bottlenecks, revealing whether CPU >80% during calls indicates overload.
For enterprise-grade stability, deploying Teams via optimize performance tools—such as Intel’s Quick Sync Video or NVIDIA’s NVENC—enhances hardware-accelerated decoding, bypassing CPU video

Related Post

Maggie Q’s Husband and Dylan McDermott’s West Hollywood Moment: A Glimpse Behind the Headlines

Discover the World of Gwyneth’s Siblings: A Tapestry of Influence, Talent, and Legacy

Unlock Ecosystem Secrets with the BiomeMapColoringWorksheet

Behind the Spotlight: The Quiet Family Life of Song Seung Heon and the Woman Who Shaped Him

