Work Authorization Under Trump’s Policies: Shaping the Future of Employment in America
Work Authorization Under Trump’s Policies: Shaping the Future of Employment in America
Under the second Trump administration, work authorization has become a pivotal fulcrum in reshaping labor access, national security priorities, and economic strategy. The policies enacted reflect a deliberate recalibration of immigration and employment systems, emphasizing merit-based selection, enhanced vetting, and tighter enforcement—changes that echo both continuity and sharp departure from prior frameworks. While framed as bolstering American workers’ protections and strengthening border control, these measures carry profound implications for industries reliant on immigrant labor, job seekers navigating complex pathways, and the balance between security and opportunity.
This analysis unpacks the core mechanisms of Trump’s work authorization agenda, its real-world impact, and the ideological currents driving its evolution.
Targeted Reforms: Redefining Eligibility and Access
Central to Trump’s approach has been a refinement of visa categories and work permit standards designed to prioritize skilled labor and reduce perceived vulnerabilities. The administration pursued.One key shift involved tightening the H-1B visa program—long criticized for enabling labor overreach in tech and professional sectors.
Proposals under reviewed employer sponsorship rules, requiring stronger proof of job uniqueness and competitive wage assessments. Similarly, adjustments to the J-1 exchange visitor program reduced funding for high-risk agricultural and seasonal work visas, aiming to limit exploitation and strengthen domestic workforce participation. Broader eligibility shifts emphasized merit-based entry.
Proposals increased points for STEM qualifications, English fluency, and advanced degrees—aligning with the vision of attracting talent that fuels innovation. Yet, protections for vulnerable workers, such as agricultural laborers and low-wage service staff, remained contentious. Designed to prevent "chain migration" and protect wage standards, these rules sometimes create unintended barriers, particularly in industries where immigrant workers form the backbone of operations.
Enhanced Vetting: Security as the Cornerstone
A defining feature of Trump’s authorization framework is the elevated focus on security screening, particularly for non-immigrant and temporary worker visas.Building on post-2017 reforms, the administration expanded biometric verification, intelligence sharing with partner nations, and blockchain-based employment eligibility tracking.
This layered approach aims to reduce fraud and unauthorized work, reducing national security risks while maintaining steady labor flows. Security reviews now trigger deeper background checks, including real-time analysis of criminal histories, fraud convictions, and ties to foreign entities.
While officials cite success in preventing bad actors, critics note that processing delays and opaque criteria hinder timely access to work—impacting employers in critical sectors like healthcare and technology.
Industry Impacts: Labor Shortages and Economic Pressures
The updated policies have triggered uneven outcomes across the U.S. economy. Industries historically dependent on immigrant labor, such as agriculture, hospitality, and construction, report acute staffing gaps.For example, California’s Central Valley—where immigrant workers comprise over 70% of farm labor—faces seasonal shortages worsening since 2025.
Employers cite shrinking talent pools and rising wage costs, with meatpacking and pest control experiencing 30%+ staff turnover. Small businesses, lacking resources to navigate complex renewals or application surcharges, suffer disproportionately.
While some sectors report accelerated automation, others struggle to scale operations, affecting consumer pricing and economic resilience. Conversely, skilled professions in tech and engineering reflect greater stability. Visa processing time reductions and improved employer pathways have slightly boosted availability.
Yet, the exclusion of non-STEM roles underscores growing labor segmentation—one where automation fills upper-tier gaps, but frontline and seasonal work remains reliant on precarious migration.
Labor Market Adaptation: Emerging Trade-Offs
Employers and workers alike adapt to new realities through diverse strategies. Industries facing shortages increasingly adopt wage incentives—offering signing bonuses, relocation packages, and improved benefits. Autonomous systems and robotics deployment accelerates in horticulture, logistics, and food processing, though full automation remains cost-prohibitive for many enterprises.Small business coalitions lobby for simplified, fee-free work authorization processes, arguing that current hurdles suppress growth. Meanwhile, worker advocates stress the risk of compounded vulnerability: expedited processes reduce due diligence, potentially exposing unauthorized migrants to exploitation despite heightened screening.
Data supports a modest but steady uptick in legal labor participation, particularly among STEM professionals.
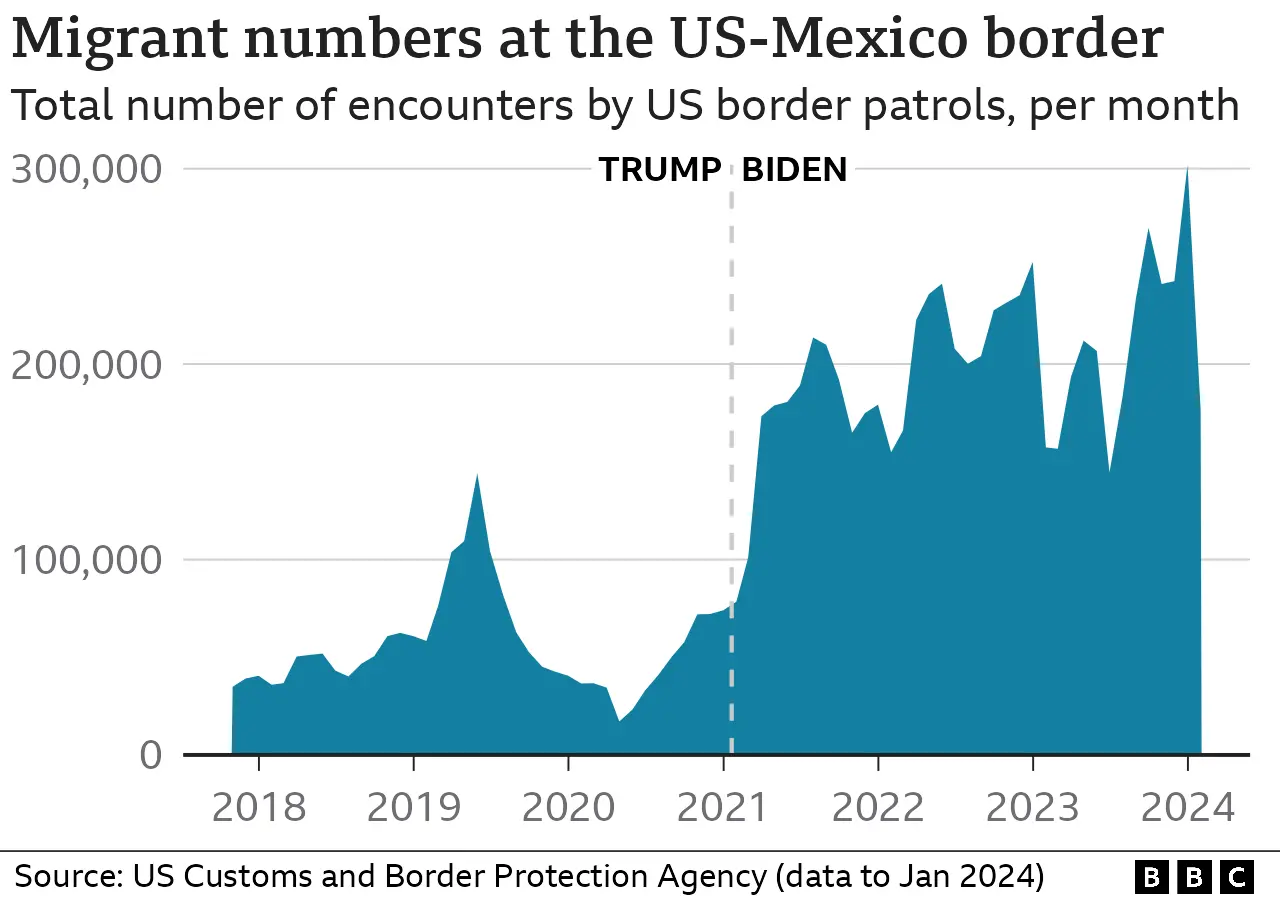
However, unauthorized work—estimated at 5–6 million people pre-2025—persists, driven by labor demand not fully met by legal channels and by economic necessity in marginalized communities. Policymakers face a tightrope between securing borders and ensuring fair, accessible pathways for legitimate work.
Policy Ideology and Long-Term Trajectory
Trump’s work authorization agenda reflects a broader ideological commitment to selective openness: welcoming talent that boosts American competitiveness and security, while restricting access where economic or security risks appear acute. This aligns with a longstanding conservative principle—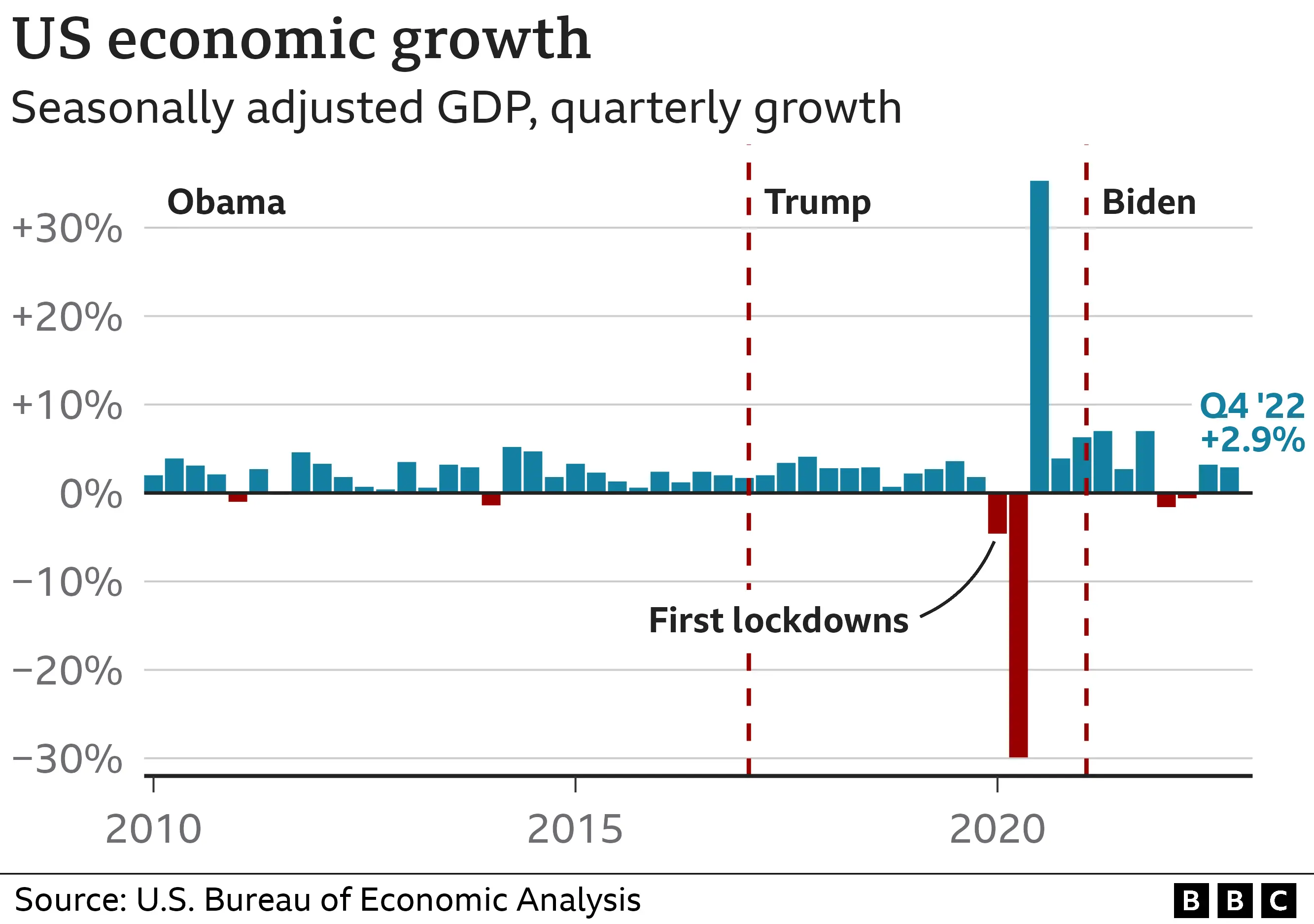


Related Post
Boost Your Voice: Master Audacity to Achieve Crystal-Clear Audio

Katie Mckee: From Grassroots Advocacy to National Podium Power

Who Played 001 in Squid Game? The Hidden Identity Behind the Second Gauger Unveiled
<strong>Login Ke YouTube Via Google Chrome: Panduan Lengkap dalam 2024</strong>

